Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes. Genes encode information for building proteins. DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents and controls the development and maintenance of organisms. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus, but small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria.
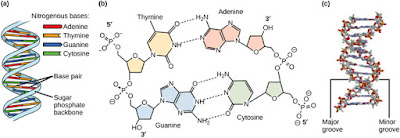
Each DNA molecule is made up two long chains arranged in a double helix. Furthemore, each link of a chain is one of four kinds of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These chemical building blocksor chemical bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (G), and thymine (T). The chemical bases pair up with each other, adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine to form bases pairs. The human DNA consists of about three billion bases. The bases are also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. The sugar and phosphate when are together they forms a nucleotide. By last, DNA can be replicate, each strand of DNA in the double helix can serve as pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases, and when cells divide each new cell needs to have an exact copy of the DNA from the old cell.
Most of this information is from https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/basics/dna

No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario